Principles of the Quality Management System


Welcome to the 4Z-Pedia. The QMS is an increasingly popular term. Whether at the level of companies, institutions, or public services. Let us delve deeper into the most important principles of the QMS to learn about its elements, and what must be fullfilled to ensure the proper establishment and sustainability of a quality culture.
1. Honesty:
- Unfortunately, you will not find this important principle included in any international quality standard or bench mark. Although honesty, in my opinion, is the most important principle that should not be ignored.
- Some might argue that honesty is an abstract moral value rather than a concrete action that can be measured and evaluated. But by experience, which is confirmed by any experienced worker, it is the common concrete factor in fulfilling true quality of any work.
- How many services or products that are only outwardly of quality, but in reality, are corrupted or mediocre. And how many institutions and companies where quality is merely a pile of documents or just a quality logo.
- Of course, when we mean honesty, we do not demand it only from the institution, but
from the body that conducts the evaluation, and from the body that grants quality certificates. That
is, from the whole system associated with the implementation, evaluation and proof of quality,
otherwise the actual quality will never be achieved at all.
Key Benefits:
- Increased credibility of the workplace and its outputs of services or products.
- Linking the behavior of employees with a moral value before the technical standard, leads to the consolidation of the principle of work perfection with an internal motive.
- Honesty of the whole system related to quality, distinguishes sooner or later the institution from others that only claim quality and do not practice it.
- All of the above surely contributes to increasing the customer base, loyalty and satisfaction.
Possible Actions:
- Consolidation of the principle of honesty in word and deed within the institution by all individuals at all levels.
- Ensuring the credibility of data, and handling it with transparency so that the organization can actually improve quality in the shortest possible time.
- Link reward and punishment to the credibility of individuals in carrying out the tasks assigned to them. And leadership must give a good example in that respect.
- Never allow advertising, marketing or selling of a product or service that meets quality standards only on paper.
- Do not punish or discriminate any employee who refuses to pass on any manipulation or fraud, that threatens the credibility of the institution, even if it is at the expense of profit.
- Always look at honesty and its returns in the long run and not with a narrow mindset that calls for profit at the expense of credibility.
- As they say a lie has short legs, so everyone should realize that neglecting honesty and credibility of quality cannot deceive the customer for a long time.
2. Customer Focus:
- Primary focus of quality management is to meet requirements of the customer & interested parties.
- Understanding current and future needs of customers & interested parties, contributes to sustained success.
- Sustained success is achieved when confidence of customers is attracted and retained.
Key Benefits:
- Increased customer value; satisfaction; loyalty; and base.
- Enhanced repeat business; reputation of the organization.
- Increased revenue and market share.
Possible Actions:
- Recognize direct and indirect customers as those who receive your product/service.
- Understand customer's current and future needs and expectations.
- Link objectives to customer needs and expectations.
- Communicate customer needs and expectations throughout the organization.
- Plan, design, develop, produce, deliver and support products and services to meet customer needs and expectations.
- Measure and monitor customer satisfaction and take appropriate actions.
- Determine and take action on relevant interested parties' needs and expectations that can affect customer satisfaction.
- Actively manage relationships with customers to achieve sustained success.
3. Leadership:
- Leaders at all levels establish unity of purpose and direction.
- Leaders create conditions in which people are engaged in achieving quality objectives.
- Creation of unity of purpose and direction and engagement of people, enables aligning strategies,
policies, processes and resources to achieve objectives.
Key Benefits:
- Increased effectiveness & efficiency in meeting organization's quality objectives.
- Better coordination of organization's processes.
- Improved communication between levels and functions of the organization.
Possible Actions:
- Communicate organization's mission, vision, strategy, policies and processes throughout the organization.
- Create and sustain shared values, fairness and ethical models for behavior at all levels of the organization.
- Establish a culture of trust and integrity.
- Encourage an organization-wide commitment to quality.
- Ensure that leaders at all levels are positive examples to people in the organization.
- Provide people with required resources, training and authority to act with accountability.
- Inspire, encourage and recognize the contribution of people.
4. Improvement:
- Successful organizations have an ongoing focus on improvement.
- Improvement is essential to maintain current levels of performance. And to react to
changes in internal and external conditions and to create new opportunities.
Key Benefits:
- Improved process performance, organizational capability and customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced focus on root cause investigation and determination, followed by prevention and corrective actions.
- Enhanced ability to anticipate and react to internal and external risks and opportunities.
- Enhanced drive for innovation.
Possible Actions:
- Identify the need for improvement and recognize their importance.
- Promote establishment of improvement objectives at all levels.
- Educate and train people at all levels on how to apply basic tools and methods to achieve improvement objectives.
- Ensure people are competent to successfully promote and complete improvement projects.
- Track, review and audit planning, implementation, completion and results of improvement improvement projects.
- Integrate improvement consideration into development of new or modified products, services and processes.
- Recognize and acknowledge improvement.
5. Process Approach:
- Consistent and predictable results are achieved more effectively and efficiently, when activities are understood and managed as interrelated processes that function as a system.
- Quality Management System consists of interrelated processes. Understanding how
results are produced by this system enables optimization of the system and its performance.
Key Benefits:
- Enhanced ability to focus effort on key processes and opportunities for improvement.
- Consistent and predictable outcomes through a system of aligned processes.
- Optimized performance through effective processes management, efficient use of resources and reduced cross-functional barriers.
- Increased confidence of interested parties, in consistency, effectiveness and efficiency of the organization.
Possible Actions:
- Define objectives of the system and processes necessary to achieve them.
- Establish authority, responsibility and accountability for managing processes.
- Understand the organization's capabilities and determine resource constraints prior to action.
- Determine process interdependencies and analyze the effect of modifications to individual processes on the system as a whole.
- Manage processes and their interrelations as a system to achieve quality objectives effectively and efficiently.
- Ensure that necessary information is available to operate and improve processes and to monitor, analyze and evaluate performance of the overall system.
- Manage risks which can affect outputs of processes and overall outcomes of the QMS.
6. Engagement of People:
- Competent, empowered and engaged people at all levels are essential to enhance the capability to create and deliver value.
- To manage an organization effectively and efficiently, it is important to respect and involve all people at all levels.
- Recognition, empowerment and enhancement of competence facilitate engagement of
people in achieving objectives.
Key Benefits:
- Improved understanding of quality objectives by people and increased motivation to achieve them.
- Enhanced involvement of people in improvement activities.
- Enhanced personal development, initiatives and creativity.
- Enhanced people satisfaction.
- Enhanced trust and collaboration throughout the organization.
- Increased attention to shared values and culture throughout the organization.
Possible Actions:
- Communicate with people to promote understanding of the importance of their individual contribution.
- Promote collaboration throughout the organization.
- Facilitate open discussion and of knowledge and experience.
- Empower people to determine constraints to performance and to take initiatives without fear.
- Recognize and acknowledge people's contribution, learning and improvement.
- Conduct surveys to assess people's satisfaction, communicate results and take appropriate actions.
7. Relationship Management:
- For sustained success, relationships with relevant interested parties, should be managed.
- Relationships with interested parties influence the performance of the organization.
- Sustainable success is more likely to come when the organization manages relationships with all interested parties and pushes them to improve their services. Thus improving the performance of the organization.
- Managing relationships with suppliers and partner networks is particularly important.
Key Benefits:
- Enhanced performance through responding to opportunities and constraints related to each interested party.
- Common understanding of objectives and values among interested parties.
- Increased capability to create value for interested parties by resources and competence and managing risks.
- A well-managed supply chain that provides a stable flow of products and services.
Possible Actions:
- Determine relevant interested parties and define their relationship with the organization.
- Interested parties can be: providers, partners, customers, investors, employees or society as a whole.
- Establish relationships that balance short-term gains with long-term considerations.
- Establish relationships that balance short-term gains with long-term considerations.
- Gather and share information, expertise and resources with relevant interested parties.
- Measure performance and provide feedback to interested parties, to enhance improvement initiatives.
- Establish collaborative development and improvement activities with interested parties.
- Encourage and recognize improvements and achievements by providers and partners.
8. Evidence-based Decision Making:
- Decisions based on analysis and evaluation of data and information are more likely to produce desired results.
- Decision-making can be a complex process and it always involves some uncertainty.
- It often involves multiple types and sources of inputs, as well as their interpretation, which can be subjective.
- Facts, evidence and data analysis, lead to greater objectivity and confidence in
decision-making.
Key Benefits:
- Improved decision-making processes.
- Improved assessment of process performance and ability to achieve objectives.
- Improved operational effectiveness and efficiency.
- Increased ability to review, challenge and change opinions and decisions.
- Increase the ability to prove the effectiveness of previous decisions.
Possible Actions:
- Determine, measure and monitor key indicators to demonstrate performance.
- Make all data needed available to relevant people.
- Ensure that data and information are sufficiently accurate, reliable and secure.
- Analyze and evaluate data and information using suitable methods.
- Ensure that people are competent to analyze and evaluate data as needed.
- Make decisions and take actions based on evidence, balanced with experience and intuition.
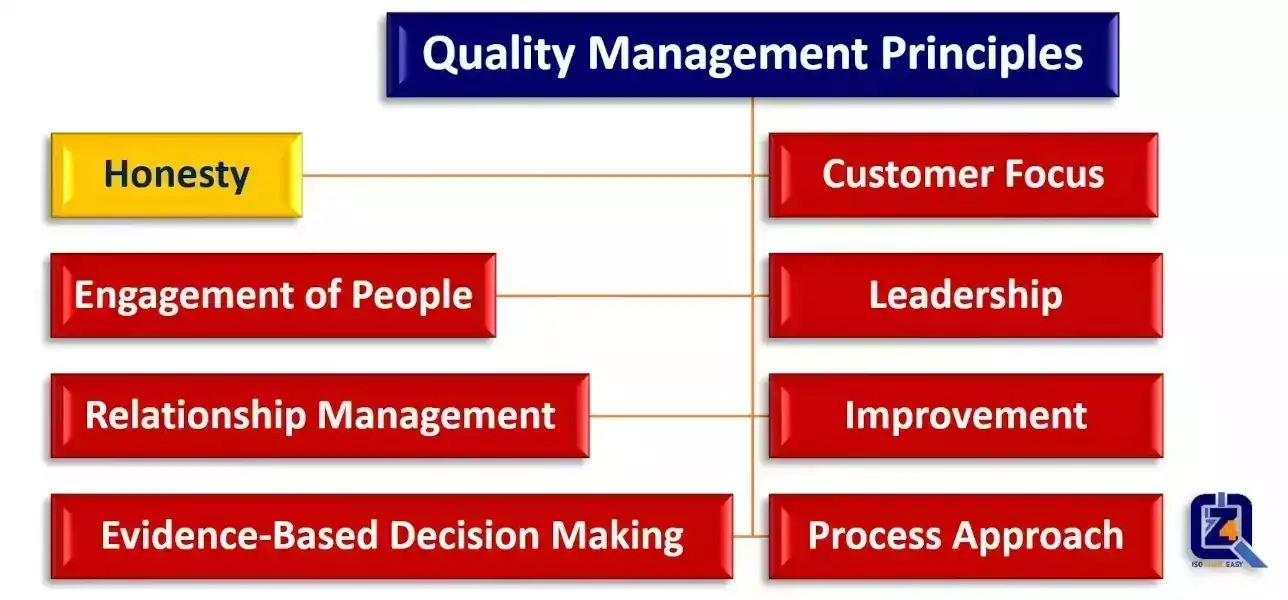
Here again are the principles of the QMS at a glance:

We have a lot more to talk about quality management systems. For all your questions, email us today at: support@the4z.com. We respond immediately, and clearly, or call 4Z for Quality today at (also on WhatsApp): +973 3399 5807 or +90 5050 3040 16.
Further Readings:
- Quality Management System
- Concepts of QMS
- ISO Standards
- Steps of ISO Certification
- Prepare for ISO Certification
- Educational Accreditation
- Strategic Planning
Videos:
External Links:
Quality Quote:
- If you can't explain (it) simply, you don't understand (it) yet well enough

